How a Tensile Testing Machine Works?
A Tensile Strength Tester (Tensile Testing Machine) is a mechanical testing instrument used to measure how materials behave when they are stretched or pulled. It helps determine how strong a material is, how much it can stretch before breaking, and how it deforms under tension.
How a Tensile Testing Machine Works
Sample Preparation: A test specimen (plastic, rubber, paper, metal, yarn, etc.) is prepared according to standard dimensions.
Clamping: The specimen is fixed between two grips – one stationary and one movable.
Applying Load: The machine pulls the specimen at a controlled speed through a motorized drive system.
Measuring Force & Elongation:
A load cell measures the force applied.
A displacement sensor records how much the specimen stretches.
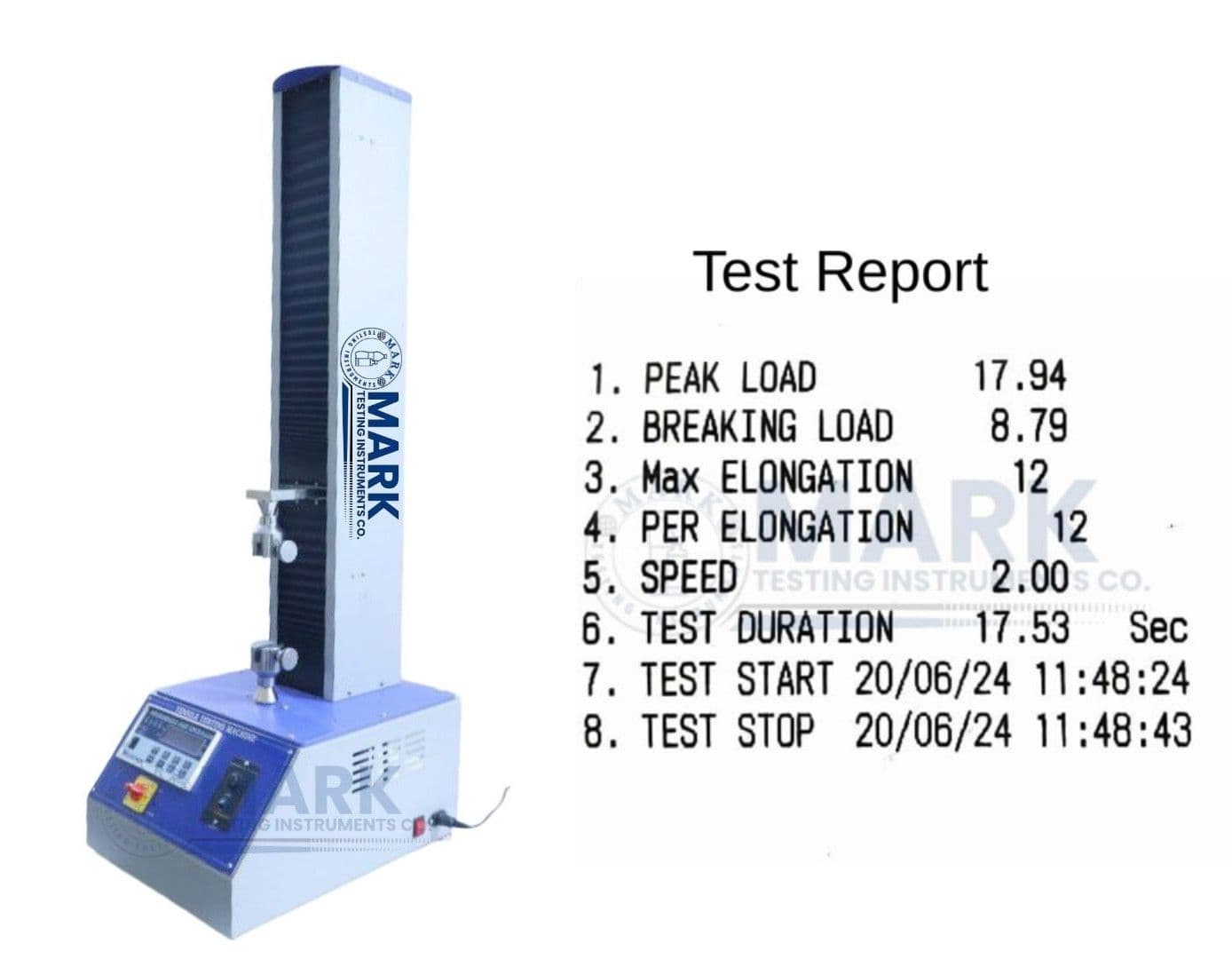
Data Display & Analysis: The system displays real-time readings of load, elongation, and tensile strength on the digital screen. Some models (like the one from Mark Testing Instruments) also print instant test reports.
Fracture Point: The test continues until the material breaks, and the machine records the peak load (breaking strength).
Why Tensile Testing is Used
Tensile testing is one of the most important mechanical tests for quality control, research, and product development. It is used to:
Determine Material Strength – Measures how much load a material can withstand before breaking.
Evaluate Elasticity & Ductility – Helps understand how flexible or brittle a material is.
Ensure Quality Control – Confirms that materials meet industry standards (ASTM, ISO, IS, etc.).
Compare Materials – Used to select suitable materials for specific applications.
Research & Development – Assists in improving material formulations and performance.
Compliance & Certification – Required for verifying product strength and durability for packaging, automotive, textile, and polymer industries.
In Simple Terms:
A tensile testing machine pulls a material until it breaks — to find out how strong, flexible, and durable it is. It’s widely used in industries like packaging, plastics, rubber, textiles, metals, and research labs to ensure materials meet safety and performance standards.